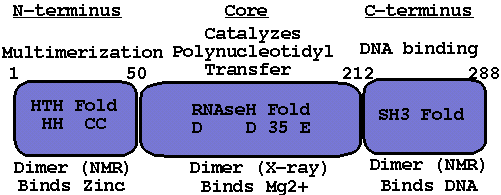
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) uses an enzyme, a so-called integrase, to carry out the integration of its viral DNA into the host chromosome thereby tricking the host cell machinery into making viral proteins. The HIV integrase is composed of three domains, as shown below.
This will be accomplished via an iterative feedback cycle of computational chemistry, organic synthesis, crystallography, and assay with each component also working along independent lines.
The computational work will be focused along two basic parallel lines of work: 1). MS simulation of full domain HIV integrase structure, and 2). pharmacophore modeling and docking.